Understanding Glufosinate-Ammonium Weed Killer: How It Works and Its Applications in Agriculture
Glufosinate-Ammonium is a non-selective broad-spectrum herbicide that has gained popularity in recent years. It is often compared to glyphosate, which is the world's most widely used herbicide. However, due to its high cost, it has not been widely adopted in agricultural production. Its primary applications are as follows:
1). High-value orchards and tea gardens for weed killing.
2). Crops with shallow root systems, such as grapes, dragon fruit, and potatoes.
3). Some crops that are tolerant to glufosinate, such as corn, soybeans, and sugar beets, which are extensively cultivated.
4). Mixing with other pesticides, especially with glyphosate and 2,4-D.
As the price of glufosinate has decreased, and more countries have started to restrict the use of glyphosate, more farmers have begun to consider glufosinate as an alternative. This article discusses How glufosinate Works and Its Applications in Agriculture.
1. Mechanism of Action of Glufosinate-Ammonium
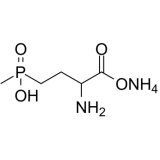
1.1 Chemical Composition and Molecular Structure: The main components of glufosinate are glufosinate acid and ammonium salt. It effectively controls the growth of various weeds while having a relatively low impact on crops. Also known as: glufosinate-ammonium, 2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)butanoic acid ammonium salt. with the following molecular formula:
1.2 How Glufosinate-Ammonium Works on Weeds and Why It Is Effective:
Glufosinate-Ammonium is a broad-spectrum contact herbicide with some limited systemic action. It targets the enzyme glutamine synthetase in plants, inhibiting its activity. This disruption leads to nitrogen metabolism imbalance, excess ammonia accumulation, chloroplast disintegration, and disruption of photosynthesis in plants, resulting in weed control. After absorption by weeds, glufosinate can be translocated within the plant via transpiration. Typically, within 3 to 5 days under normal conditions, the weeds gradually wither and die, with a lasting effect of around 30 days. Unlike glyphosate, which kills roots, glufosinate initially targets leaves and can be translocated within the woody parts of the plant through transpiration. Its speed of action falls between paraquat and glyphosate.
2. Applications in Agriculture
2.1 Used in Various Types of Fields:
Glufosinate can be used in orchards, vineyards, non-cultivated land for weed control, as well as in potato fields to control annual and perennial dicot and monocot weeds and sedges, such as Setaria viridis, Echinochloa crus-galli, Solanum nigrum, Digitaria sanguinalis, wild oats, wild corn, Elymus repens, etc. The application rate varies depending on the crop and weeds, ranging from 1 to 2 kg per hectare or more, such as for controlling weeds like Solanum nigrum and ferns in forests and highland pastures, where the rate can range from 1.5 to 20 kg per hectare.
2.2. Actual Effects of Glufosinate-Ammonium on Weed Control and Comparison with Glyphosate:
|
Experimental conditions |
200g/L glufosinate formulation VS 41% glyphosate isopropylamine salt |
|
Location |
Hengyang, Hunan, China |
|
Application method |
Foliar spray |
|
Application rates |
200g/L glufosinate: 500g/acre, 400g/acre; 41% glyphosate isopropylamine salt: 500ml/acre. |
|
Application background |
August 23rd, a clear, windless day with a temperature of 30°C. |
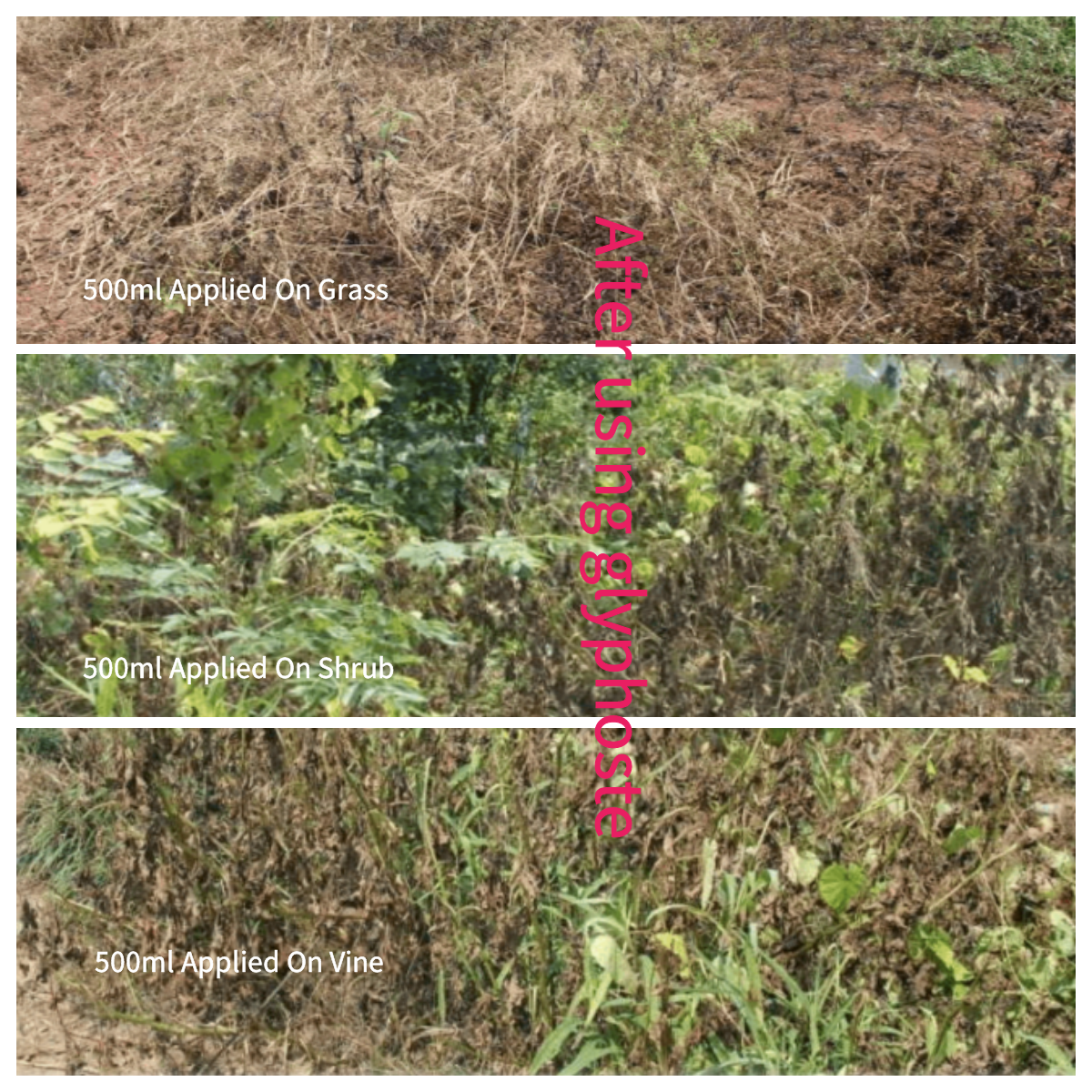
Observations on the seventh day after application: Weeds at the sprayed locations had completely died, showing symptoms of yellowing and withering. The 500g/acre application rate clearly outperformed the 400g/acre rate. Notably, glufosinate exhibited excellent performance on the most challenging vine-like plants, causing complete death in treated plants. Compared to glyphosate, the 400g/acre glufosinate application had a faster and more thorough effect than the 500ml/acre glyphosate isopropylamine salt.
In conclusion:
1). The 200g/L glufosinate water-based formulation performed well at both 400g/acre and 500g/acre application rates, showing good efficacy against common weeds, grasses, small shrubs, and vines. In situations with fewer and less dense weeds, there was not much difference between the two doses. However, in more complex and weed-dense conditions, the 500g/acre dose significantly outperformed the 400g/acre dose. Therefore, in areas with complex weed situations and high weed density, a higher dosage is recommended.
In conclusion:
1). The 200g/L glufosinate water-based formulation performed well at both 400g/acre and 500g/acre application rates, showing good efficacy against common weeds, grasses, small shrubs, and vines. In situations with fewer and less dense weeds, there was not much difference between the two doses. However, in more complex and weed-dense conditions, the 500g/acre dose significantly outperformed the 400g/acre dose. Therefore, in areas with complex weed situations and high weed density, a higher dosage is recommended.
2). Below are some comparison photos taken during the experiment. Seven days after applying 41% glyphosate isopropylamine salt, weeds were still alive and had a poor effect on small shrubs and vine plants. In contrast, glufosinate, even at equivalent or lower doses, killed all weeds within seven days, with their roots decomposed, and it had a good effect on small shrubs and vines as well.
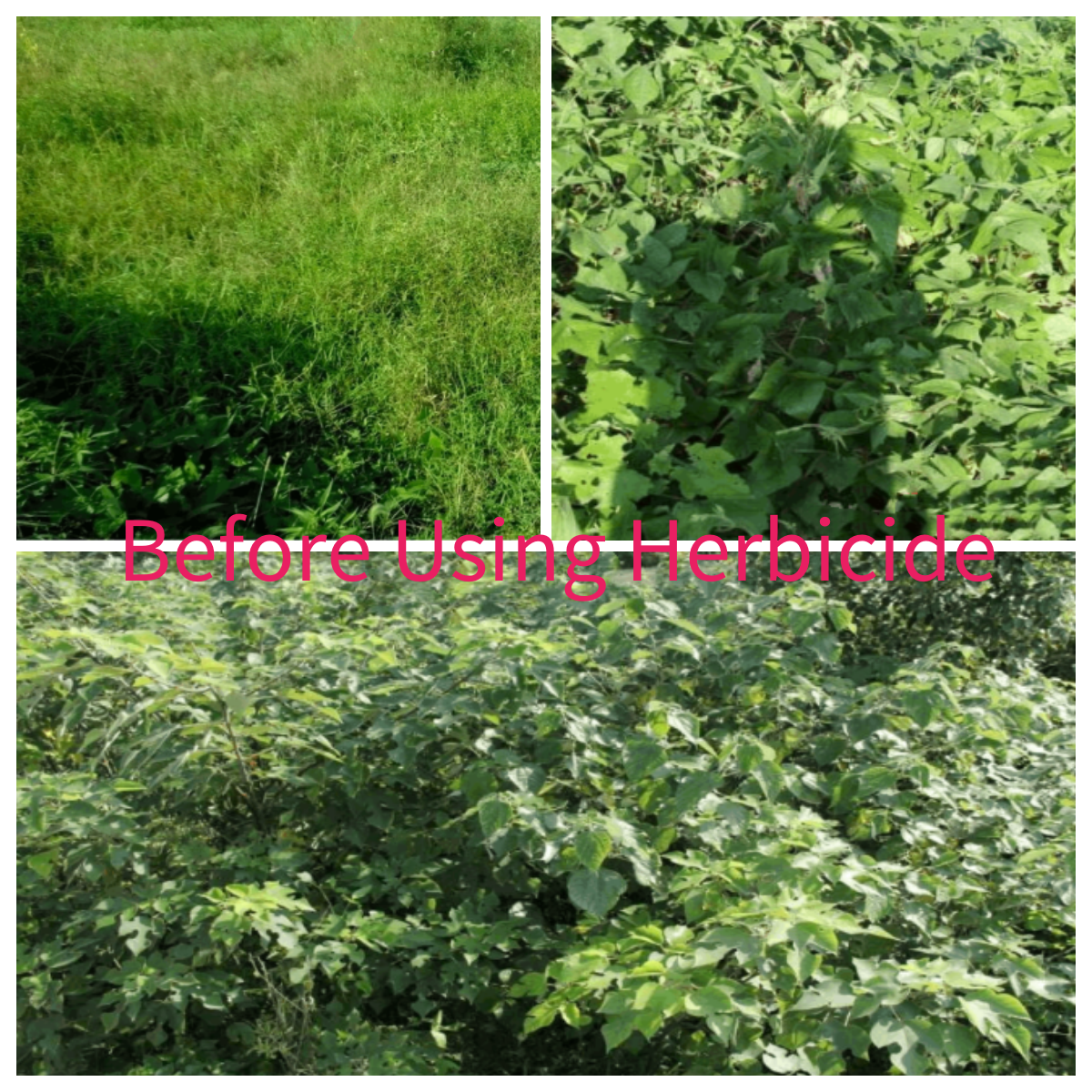
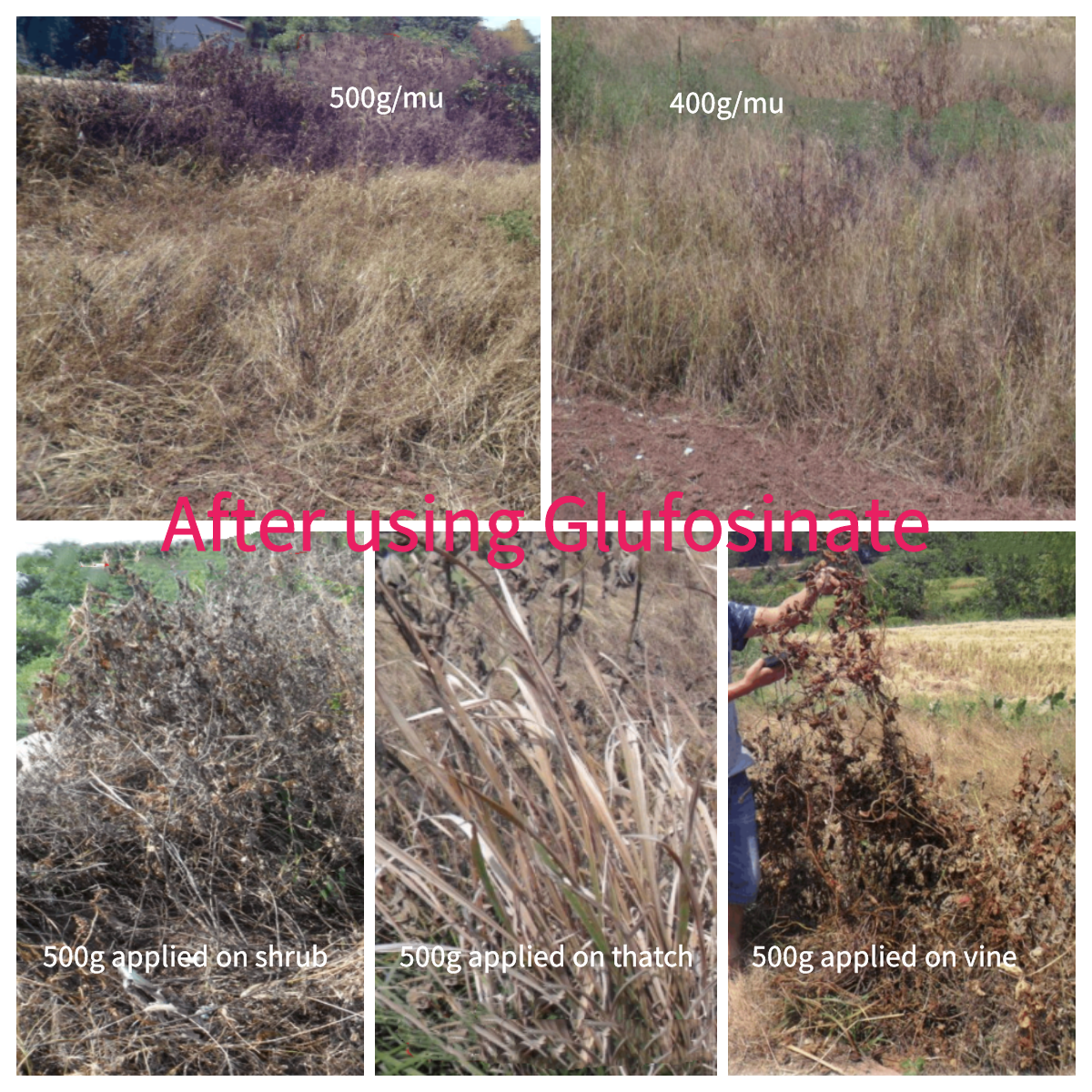



3. Advantages of Using Glufosinate-Ammonium for Crops:
3.1. Fast weed control: Weeds stop growing one day after application, turn yellow in three days, die in seven days, and reach the peak of herbicidal efficacy in 15 days. The speed of weed control is significantly faster than glyphosate, which takes ten days.
3.1. Fast weed control: Weeds stop growing one day after application, turn yellow in three days, die in seven days, and reach the peak of herbicidal efficacy in 15 days. The speed of weed control is significantly faster than glyphosate, which takes ten days.
3.2. Long-lasting effect: Glufosinate-Ammonium can remain effective for up to 25 days during the rainy season and up to 45 days during the dry season. This is 3-4 times longer than the control time of paraquat, resulting in fewer applications and labor savings.
3.3. Crop safety and wide application: Glufosinate-Ammonium leaves no residual activity in the soil and has relatively weak systemic activity. This ensures the safety of crops and subsequent crops, with minimal potential for drift damage. It can be used for weed control in all crops that can be sprayed in row spaces, including wood, vegetables, corn, tobacco, field bunds, and stubble destruction.
3.3. Crop safety and wide application: Glufosinate-Ammonium leaves no residual activity in the soil and has relatively weak systemic activity. This ensures the safety of crops and subsequent crops, with minimal potential for drift damage. It can be used for weed control in all crops that can be sprayed in row spaces, including wood, vegetables, corn, tobacco, field bunds, and stubble destruction.
4. Environmental and Safety Considerations:
Glufosinate-Ammonium is considered environmentally friendly. Degradation rates in different soils vary, with a 50.3% degradation rate in loamy soil on the fifth day, 24.7% in sandy soil, 26.6% in silty soil, and 8.2% in clay soil. After 61 days, the degradation rate in loamy soil was 99.4%, while it was 81.9% in sandy soil, 95.2% in silty soil, and 88.7% in clay soil, indicating it is easy to degrade. During application, the following precautions should be taken:
1) Avoid drift of the pesticide onto nearby crops to prevent damage.
1) Avoid drift of the pesticide onto nearby crops to prevent damage.
2) Use protective shields when row spacing is less than 75cm to prevent drift onto crops.
3) Exercise caution near silkworms and mulberry orchards due to moderate toxicity.
4) Glufosinate-Ammonium is a toxic substance, so proper protective measures such as gloves and masks should be worn to avoid skin contact and inhalation of fumes.
5) Avoid spraying Glufosinate-Ammonium near water bodies and water sources to prevent environmental pollution.
6) Keep Glufosinate-Ammonium away from food, beverages, medicines, and other easily contaminated items to prevent ingestion or misuse.
7) After spraying Glufosinate-Ammonium, restrict access of people and animals to the treated area to avoid contact and potential harm.
8) When using Glufosinate-Ammonium, comply with relevant national laws, regulations, and safety guidelines.
Latest News
Contact Us

Name: Kim Gong
Tel: +86-15150222860 , +86-18015677881
E-mail: [email protected]
Skype: kim.gong
QQ: 326296678
WeChat: +8615150222860
Whatsapp: +8615150222860
Add: No.268, Jingang Road, Zhangjiagang Free Trade Zone, Zhangjiagang City, Jiangsu Province, China
 CHINESE
CHINESE ENGLISH
ENGLISH




 Skype Chat
Skype Chat WhatsApp
WhatsApp  Mail inquiry
Mail inquiry QQ online
QQ online
